About Radon
WHAT IS RADON
Radon is a naturally occurring, odorless, colorless, tasteless, radioactive gas produced from the radioactive decay of radium, found in most soils and earthen construction materials. Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the U.S. after smoking, and the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency estimates that radon is responsible for more than 21,000 lung cancer deaths per year.
Radon is a naturally occurring, odorless, colorless, tasteless, radioactive gas produced from the radioactive decay of radium, found in most soils and earthen construction materials. Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer in the U.S. after smoking, and the leading cause of lung cancer among non-smokers. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency estimates that radon is responsible for more than 21,000 lung cancer deaths per year.
|
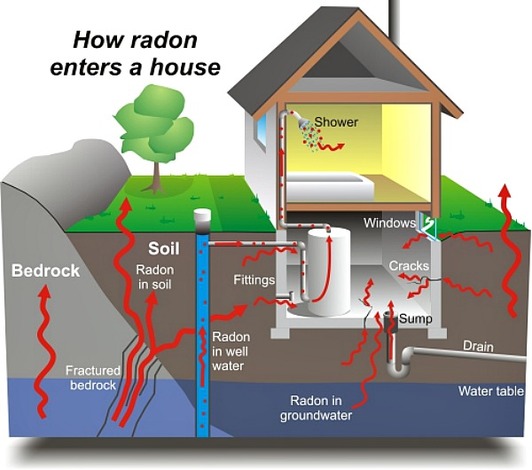
HOW DOES RADON GET IN YOUR HOME
Radon comes from the natural decay of uranium that is found in nearly all soils. It typically moves up through the ground to the air above and into your home through cracks and other holes in the foundation. Your home traps radon inside, where it can build up. Any home may have a radon problem. This means new and old homes, well-sealed and drafty homes, and homes with or without basements. Radon from soil gas is the main cause of radon problems. Sometimes radon enters the home through well water. In a small number of homes, the building materials can give off radon, too. However, building materials rarely cause radon problems by themselves. RADON GETS IN THROUGH:
|
WHAT IS RADON MITIGATION
Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer, and the number one cause of lung cancer in non-smokers. Radon mitigation refers to methods used to lower the level of radon gas in our homes. If elevated radon levels were detected through radon testing, and repaired, we could in theory prevent 20,000 deaths from lung cancer in the United States each year. I am often asked the question: “Can’t I just open windows to lower the level of radon in my home?” Unfortunately, keeping our families safe from the cancer causing effects of radon gas is not that simple.
Radon is the second leading cause of lung cancer, and the number one cause of lung cancer in non-smokers. Radon mitigation refers to methods used to lower the level of radon gas in our homes. If elevated radon levels were detected through radon testing, and repaired, we could in theory prevent 20,000 deaths from lung cancer in the United States each year. I am often asked the question: “Can’t I just open windows to lower the level of radon in my home?” Unfortunately, keeping our families safe from the cancer causing effects of radon gas is not that simple.
WHEN IS RADON MITIGATION RECOMMENDED
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends fixing your home if the radon level is above 4 pCi/L (pico Curies per Liter). They also state that individuals should consider repairs if the level falls between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L. According to the EPA, there is no level of radon gas in our homes that is considered safe, but the United States Congress has defined a long-term goal of having radon levels in homes no greater than the average radon level in outdoor air — 0.4 pCi/L. Currently, the average radon level inside homes in the U.S. is 1.3 pCi/L.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) recommends fixing your home if the radon level is above 4 pCi/L (pico Curies per Liter). They also state that individuals should consider repairs if the level falls between 2 pCi/L and 4 pCi/L. According to the EPA, there is no level of radon gas in our homes that is considered safe, but the United States Congress has defined a long-term goal of having radon levels in homes no greater than the average radon level in outdoor air — 0.4 pCi/L. Currently, the average radon level inside homes in the U.S. is 1.3 pCi/L.